Showing 1 - 2 of 2
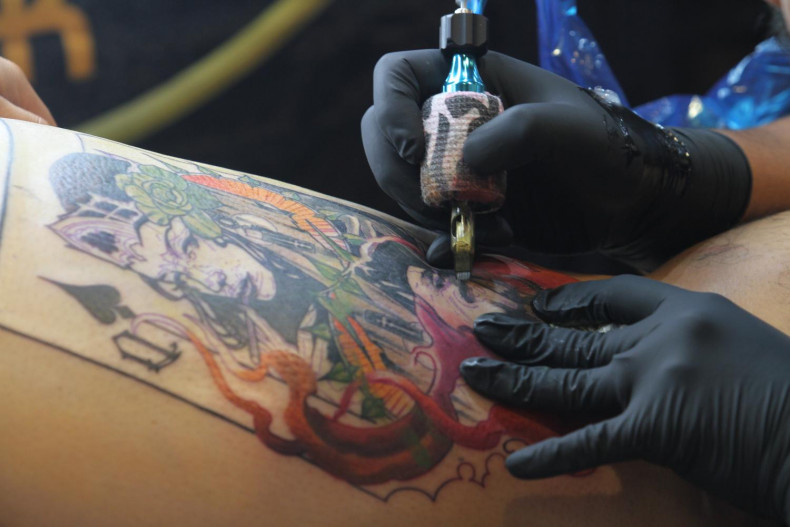
Could a simple tattoo be able to cure what ails you?
Oped, Anh Diep, Published on 01/10/2022
» Tattoos and medicine may seem an unlikely pairing, but medical tattoos are nothing new. Religious tattoos of ancient Egyptians honoured the gods and, possibly, directed divine healing to ailing body parts. Circa 150 CE, Galen, a Greek physician working in the Roman Empire, tattooed pigment onto patients' corneas to reduce glare and improve their eyesight. Modern doctors have also used tattoos in reconstructive and cosmetic procedures to disguise scars and restore the appearance of lost body parts, such as nipples for mastectomy patients.
Don't forget about viral hepatitis
Oped, Poonam Khetrapal, Published on 29/07/2021
» The World Health Organization (WHO) Southeast Asia region is intensifying action to eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030. Globally, an estimated 296 million people live with chronic hepatitis B and around 58 million live with chronic hepatitis C. In 2019, viral hepatitis caused nearly 1.1 million deaths globally, despite the existence of safe and effective vaccines that can prevent hepatitis B and antiviral drugs that can manage chronic hepatitis B and cure most cases of hepatitis C. An estimated 60 million people in the region live with chronic hepatitis B and around 10.5 million live with chronic hepatitis C. In 2019, around 180,000 people in the region died of hepatitis B and about 38,000 died of hepatitis C -- both completely manageable.