Showing 1 - 10 of 12
Southeast Asia amid the US-China rift
Oped, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 03/10/2025
» The rivalry between the United States and China has become the defining contest of the 21st century. Barely two decades ago, Washington and Beijing were partners in prosperity. America's support for China's entry into the World Trade Organization in 2001 epitomised the high-water mark of engagement, reflecting the belief that economic integration would lead to greater political cooperation. Today, that partnership has morphed into suspicion and confrontation. Relations between the United States and China have deteriorated so swiftly that many observers now describe them as locked in a "new Cold War". The more pressing question, however, is not whether this analogy holds, but whether confrontation can be managed short of outright conflict.
What's happened to the Asian Century?
Oped, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 14/02/2025
» Until recently, the "Asian Century" seemed a compelling narrative but now it is not what it used to be. It was supposed to herald a shift in global economic power from the West to the East, driven by China's rapid rise, India's economic dynamism, and the broader development of Asia. But a quarter of the way into the 21st century, the promise of Asian dominance appears less certain. The enduring technological and economic might of the United States, coupled with its geopolitical backlash against China, has lowered expectations. While Asia remains formidable, the trajectory of global power is open and fluid, with potential dominance shifting not necessarily to any nation or region but perhaps to a non-state entity.
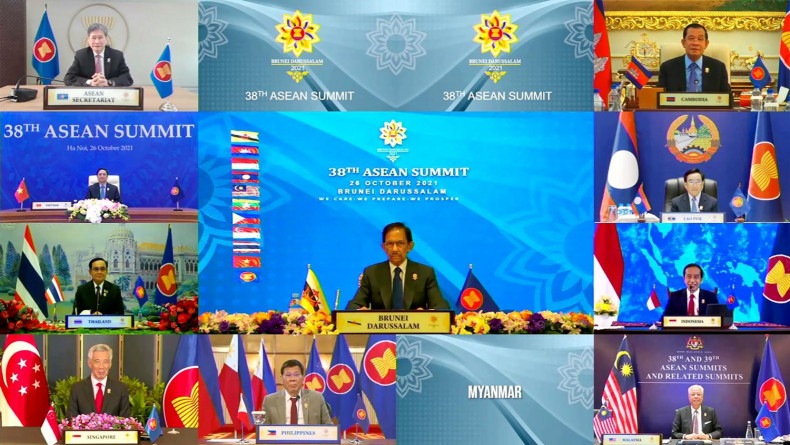
What happens if Asean shrinks to 9?
Oped, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 29/10/2021
» It all came down to a choice between marginalisation and irrelevance on the one hand and pragmatism and resilience on the other. At its 38th and 39th leaders' meetings and related summits with dialogue partners, Asean chose to remain relevant. In an unprecedented move with far-reaching ramifications, Asean reduced itself to nine participating members from the normal 10, excluding Myanmar. While this bold manoeuvre derived from necessity rather than initiative, it provides Southeast Asia's bloc of smaller states a small window of opportunity to regain its footing and revitalise its central role in promoting regional peace and stability in Asia.
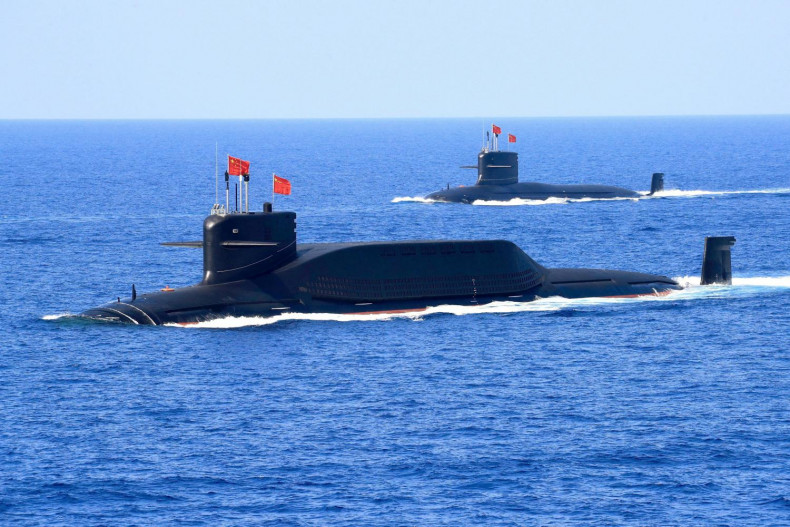
Aukus poses challenges to other powers
Oped, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 15/10/2021
» The Australia-United Kingdom-United States (Aukus) security pact has caused ripple effects across oceans and continents. Not only will the trilateral security partnership provoke China, but it will likely further divide Southeast Asia and overshadow Asean-centred cooperative vehicles, such as the East Asia Summit. Beyond these concerns, the Aukus deal to share Anglo-American nuclear technology to enable Australia's acquisition of eight nuclear-powered submarines over two decades poses challenges to other major powers, particularly the European Union and its key members as well as Japan.
Aukus pact raises geopolitical tensions
Oped, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 08/10/2021
» In less than a month, the trilateral security partnership among Australia, the United States and the United Kingdom (Aukus) has stolen the thunder from other geostrategic schemes that have been around for over a decade.
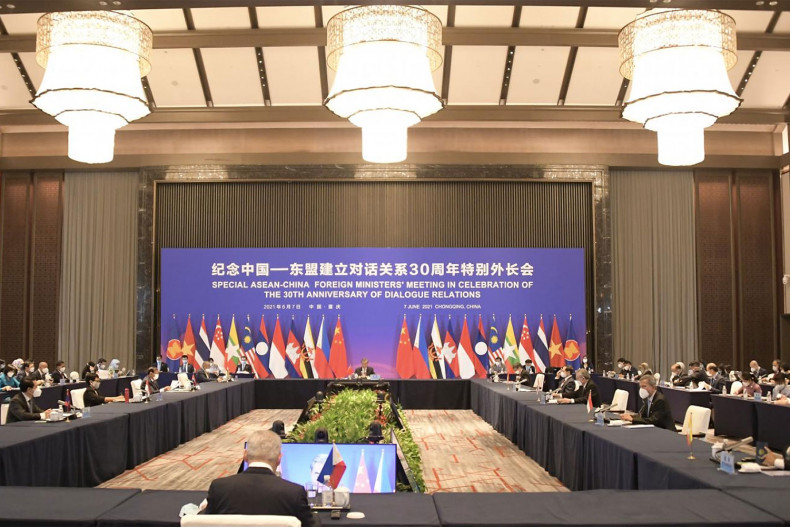
China's way with a divided, inert Asean
Oped, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 18/06/2021
» The recent Asean-China foreign ministers' meeting early this month in Chongqing was crucial for its timing and circumstances. Co-chaired by Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi and Philippine Foreign Secretary Teodoro Locsin, it was the first "in-person" meeting among foreign ministers of both sides since the Covid-19 period began early last year.
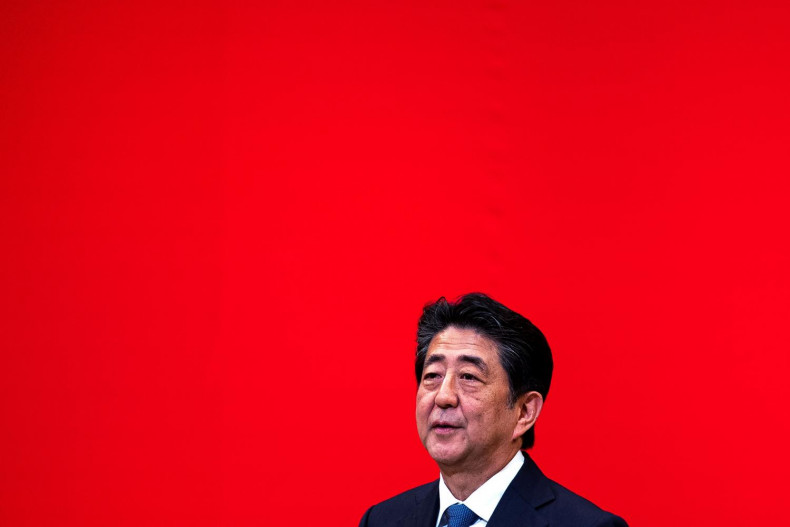
Abe legacy is Japan as 'normal' nation
Oped, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 04/09/2020
» Japan's outgoing Prime Minister Shinzo Abe will be missed throughout much of Asia, including China. His health-induced political departure attributable to a recurrence of ulcerative colitis brings to an end Japan's longest-serving prime minister in a consecutive tenure. While much will be recorded about his rich legacy, Mr Abe should be seen as a natural mover and shaker who reshaped Japan into a more "normal" country able to pursue its national interest like others by all available means.
Asean must unite to resolve Covid-19
News, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 27/03/2020
» As the Covid-19 pandemic runs its course and wreaks havoc worldwide, the numbers look bleak. Nearly 500,000 people have been infected, and more than 21,000 had died as of Thursday. The international system has reverted to every country for itself, as borders have gone up and globalisation has come down. The world as we knew it is unlikely to be the same, but regions as they were remain relevant. Here, Asean, as Southeast Asia's regional bloc, must face up to the crisis together or risk being torn apart by it.
Where Northeast, Southeast Asia meet
News, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 13/12/2019
» That the post-Second World War liberal international order is unravelling is no longer in dispute. While there are ongoing issues and challenges about how and to what extent the incumbent rules-based international order that has been so beneficial to so many nations and peoples in their course of economic development can still be maintained, there is broad agreement that the international system as we know it has run its course.
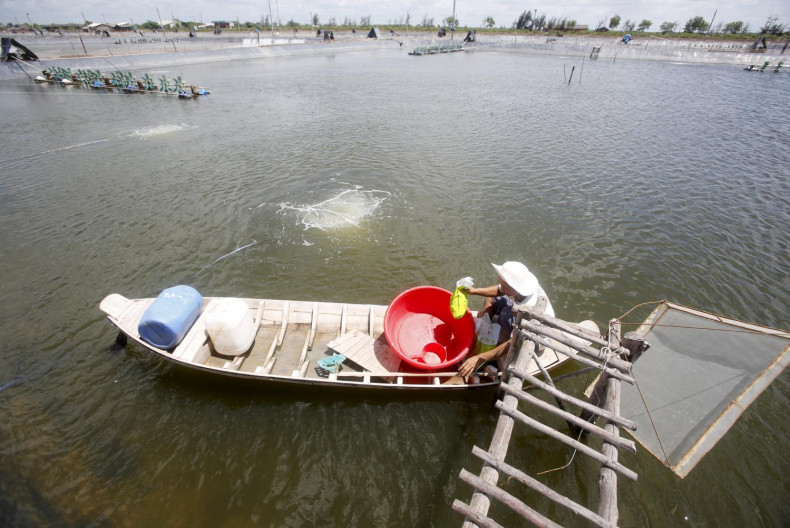
Mekong River region on more minds
News, Thitinan Pongsudhirak, Published on 06/12/2019
» As Vietnam is poised to take over the rotational chair of Asean in January 2020, its second foremost foreign policy priority after the South China Sea is reportedly the Mekong River region. While the South China Sea, where more than one third of global shipping passes, is considered an overall Asean concern, the Mekong region is left to the five riparian countries in mainland Southeast Asia to deal with in view of China's upstream hydropower dams that have led to frequent droughts and depleted fish stocks in downstream communities, especially in Cambodia and Vietnam.